contents
What is a Cyber security definition, type and examples?
What is a network security and type?
What is application security and types?
What is a IoT (Internet of Things) security, for example?
What is Ethical Hacking, types, and what example?
Cyber security advantages and disadvantages.
What is a Basic framework network protection?
What is firewall for important cyber security?
What is a role encryption in cyber security?
What is a cyber security executive order?
Top ten future careers in cyber security.
What is a role coding in cyber security?
[A]. WHAT IS NETWORK SECURITY?
Network Security includes access control, infection and antivirus programming, application security, network investigation, kinds of organization related security (endpoint, web, remote), firewalls, VPN encryption and then some.
[B]. ADVANTAGES OF NETWORK SECURITY.
Network Security is imperative in safeguarding client information and data, keeping shared information secure and guaranteeing dependable access and organization execution as well as insurance from digital dangers. An all-around planned network security arrangement lessens upward costs and defends associations from expensive misfortunes that happen from an information break or other security occurrence. Guaranteeing genuine admittance to frameworks, applications and information empower business tasks and conveyance of administrations and items to clients.
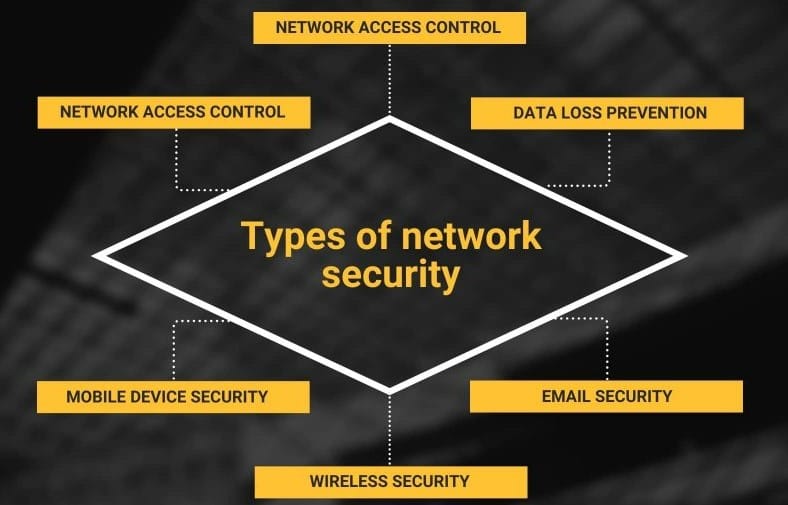
[C]. TYPES OF NETWORK SECURITY PROTECTIONS.
(1). Firewall
Firewalls control approaching and active traffic on networks, with foreordained security rules. Firewalls keep out hostile traffic and are a vital piece of day to day processing. Network Security depends intensely on Firewalls, particularly Next-Generation Firewalls, which centre around impeding malware and application-layer assaults.
(2). Network Segmentation
Network division characterizes limits between network fragments where resources inside the gathering have a typical capacity, hazard or job inside an association. For example, the edge door sections an organization network from the Internet. Possible dangers outside the organization are forestalled, guaranteeing that an association’s delicate information stays inside. Associations can go further by characterizing extra inward limits inside their organization, which can give further developed security and access control.
{The different types of network security include}
#1) Antivirus and Anti-malware Software:
The security programming that is utilized to safeguard our framework from infections, Trojan assaults, worms and so on is an antivirus against malware programming.
This product filters the framework and organization for malware and Trojan assault each time when another record is presented in the framework. It additionally identifies and fixes the issue, whenever found with any tainted information or with an infection.
#2) Data Loss Prevention (DLP):
The MNC or huge scope associations, keep up with the secrecy of information and assets by ensuring that their inward data won’t be spelt out by any of the representatives to the rest of the world.
This is finished by conveying DLP innovation in which the organization chairman confines the worker’s admittance to the data to keep it from sharing to the rest of the world by hindering ports and locales for sending, transferring or in any event, printing data.
#3) Email Security:
The aggressors can incite the infection or malware in the organization by sending it through an email in the framework.
Thusly an exceptionally gifted email security application that can check the approaching directives for infections and is fit for sifting dubious information and controlling the surge of messages to forestall any sort of data misfortune to the framework is required.
#4) Firewalls:
These are basic pieces of the systems administration framework. It goes about as a divider between two organizations or between two gadgets. It is essentially a bunch of pre-characterized rules which are utilized to keep the organization from any unapproved access.
Firewalls are of two sorts, for example, equipment, and programming. The product firewall is introduced in the frameworks to arrange safeguard from different kinds of assaults as they channel, square and fix the undesirable animals in the organization.
The equipment firewall goes about as an entryway between two systems administration frameworks so just a specific pre-characterized client or traffic can get to the organization and its assets.
Interruption counteraction framework (IPS): It is the organization’s security framework that contains some arrangement of rules and by keeping them you can undoubtedly sort out the dangers and square them also.
#5) Mobile Security:
The digital hoodlums can undoubtedly hack or assault the versatile handsets with the information office on the handsets, and they can go into the gadget from any unstable asset interface from the site.
Consequently, it is important to introduce an antivirus on our gadgets and individuals ought to download or transfer the information from dependable assets and that too from got sites as it were.
#6) Network Segmentation:
From the security perspective, a product based association will portion their vital information into a few sections and keep them in different areas and on a few assets or gadgets.
This is done, so that in the most pessimistic scenario, assuming the information in any area is defiled or erased by an infection assault, then it tends to be again recreated from any reinforcement sources.
#7) Web Security:
Web security alludes to provisioning restricted admittance to sites and URLs by obstructing the locales which are more powerless against infections and programmers. In this way, it is essentially worried about controlling the online dangers.
#8) Endpoint Security:
In the systems administration framework wherein a client is present at the remote end, getting to the urgent information base of the association from a far off gadget like cell phones or workstations, endpoint security is required.
Different programming which has inbuilt-progressed endpoint security includes and is utilized for this reason. This gives seven layers of safety comprehensive of document notoriety, auto-sandbox, web-sifting, antivirus programming, and a firewall.
#9) Access Control:
The organization ought to be planned in a manner by which not every person can get to every one of the assets.
This is finished by sending a secret word, remarkable client ID and validation process for getting to the organization. This interaction is referred to as access control as by executing it we have some control over the admittance to the organization.
#10) Virtual Private Network (VPN):
A framework can be made profoundly secure by utilizing VPN networks in relationship with involving encryption techniques for validation and drifting information traffic over the Internet to a somewhat associated gadget or organization. IPSec is the most regularly utilized confirmation process.
[D]. WHAT IS ACCESS CONTROL?
Access control characterizes individuals or gatherings and the gadgets that approach network applications and frameworks subsequently denying unsanctioned access, and perhaps dangers. Combinations with Identity and Access Management (IAM) items can emphatically distinguish the client and Role-based Access Control (RBAC) approaches to guarantee the individual and gadget are approved admittance to the resource.
(1). Remote Access VPN
Remote access VPN gives remote and secure admittance to an organization to individual hosts or clients, like remote workers, versatile clients, and extranet purchasers. Each host commonly has VPN client programming stacked or utilizes an electronic client. Security and uprightness of touchy data are guaranteed through multifaceted validation, endpoint consistence examining, and encryption of every sent datum.
(2). Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
The zero-trust security model expresses that a client ought to just have the entrance and consent that they expect to satisfy their job. This is a different methodology from that given by conventional security arrangements, like VPNs, that award a client full admittance to the objective organization. Zero trust network access (ZTNA) otherwise called programming characterized edge (SDP) arrangements licenses granular admittance to an association’s applications from clients who expect that admittance to play out their obligations.
(3). Email Security
Email security alludes to any cycles, items, and administrations intended to safeguard your email records and email content protected from outer dangers. Most email specialist co-ops have inherent email security highlights intended to keep you secure, yet these may not be to the point of preventing cybercriminals from getting to your data.
(4). Information Loss Prevention (DLP)
Information misfortune counteraction (DLP) is a network safety procedure that consolidates innovation and best practices to forestall the openness of touchy data outside of an association, particularly controlled information like actually recognizable data (PII) and consistence related information: HIPAA, SOX, PCI DSS, and so on.
(5). Interruption Prevention Systems (IPS)
IPS advances can recognize or forestall network security goes after, for example, beast force assaults, Denial of Service (DoS) assaults and exploits of known weaknesses. A weakness is a soft spot for example in a product framework and an adventure is an assault that uses that weakness to deal with that framework. At the point when an endeavour is declared, there is regularly an open door for aggressors to take advantage of that weakness before the security fix is applied. An Intrusion Prevention System can be utilized in these cases to impede these assaults rapidly.
(6). Sandboxing
Sandboxing is a network protection practice where you run code or open records in a protected, disconnected climate on a host machine that imitates end-client working conditions. Sandboxing notices the documents or code as they are opened and searches for a vindictive way of behaving to keep dangers from getting into the organization. For instance malware in documents, for example, PDF, Microsoft Word, Excel and PowerPoint can be securely distinguished and hindered before the records arrive at a clueless end client.
(7). Hyperscale Network Security
Hyperscale is the capacity of engineering to scale properly, as the expanded request is added to the framework. This arrangement incorporates quick sending and increasing or down to meet changes in network security requests. By firmly incorporating organizing and process assets in a product characterized framework, it is feasible to use all equipment assets accessible in a grouping arrangement completely.
(8). Cloud Network Security
Applications and responsibilities are not generally only facilitated on-premises in a nearby server farm. Safeguarding the cutting edge server farm requires more prominent adaptability and development to stay up with the movement of use responsibilities to the cloud. Programming characterized Networking (SDN) and Software-characterized Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) arrangements empower network security arrangements in private, public, crossover and cloud-facilitated Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) organizations.
[E]. STRONG NETWORK SECURITY WILL PROTECT AGAINST.
1). Virus: An infection is a malevolent, downloadable document that can lay lethargic that recreates itself by changing other PC programs with its code. When it spreads those records are contaminated and can spread starting with one PC then onto the next, or potentially bad or obliterate organization information.
2). Worms: Can dial back PC networks by gobbling up transfer speed as well as the sluggish effectiveness of your PC to deal with information. A worm is an independent malware that can proliferate and work freely on different records, where an infection needs a host program to spread.
3). Trojan: A trojan is a secondary passage program that makes a doorway for malignant clients to get to the PC framework by utilizing what resembles a genuine program, however rapidly ends up being destructive. A trojan infection can erase documents, initiate other malware concealed on your PC organization, like an infection and take significant information.
4). Spyware: Much like its name, spyware is a PC infection that assembles data about an individual or association without their express information and may send the data accumulated to an outsider without the buyer’s assent.
5). Adware: Can divert your hunt solicitations to publicizing sites and gather showcasing information about you in the process so that altered promotions will be shown in the view of your inquiry and purchasing history.
6). Ransomware: This is a kind of trojan cyberwar that is intended to acquire cash from the individual or association’s PC on which it is introduced by scrambling information so it is unusable, obstructing admittance to the client’s framework.
[H]. EXAMPLES OF NETWORK DEVICES
1). Desktop computers, laptops, mainframes, and servers.
2). Consoles and thin clients.
3). Firewalls
4). Bridges
5). Repeaters
6). Network Interface cards
7). Switches, hubs, modems, and routers.
8). Smartphones and tablets.
9). Webcams (cyber security)